Projects
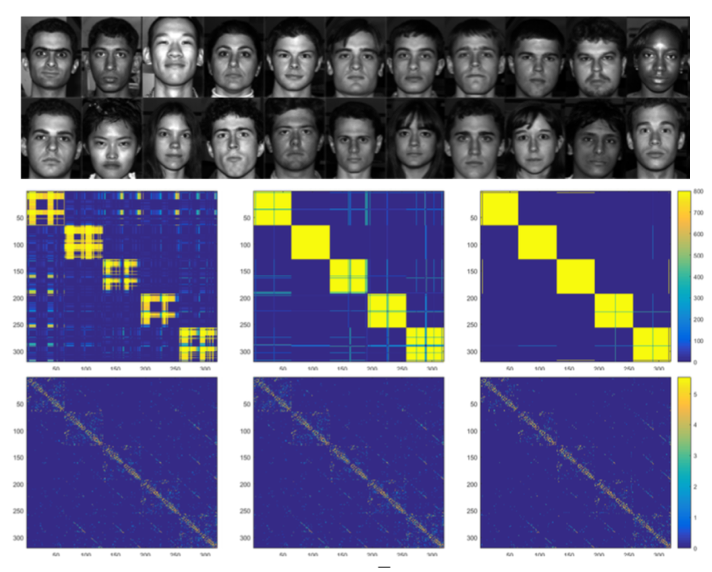
Probabilistic Sparse Subspace Clustering Using Delayed Association
We introduced a new subspace clustering method by replacing the usual clustering matrix with an association matrix A that allows us to track the assignment of points in the same clusters, and hence delay hard assignments until later iterations, when more confidence is gained. The results on both synthetic and real data confirm these advantages.
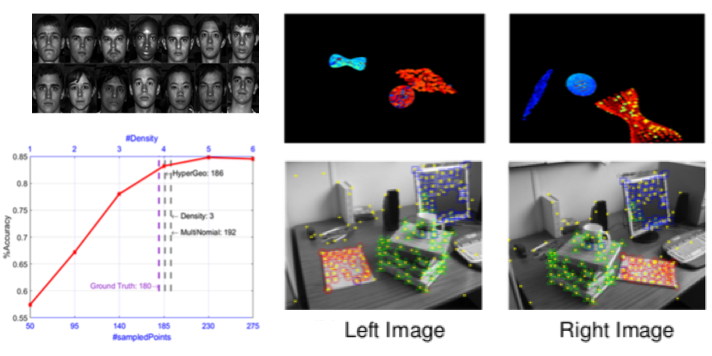
Sparse One Grab Sampling with Guarantees
Sampling is an important and effective strategy in analyzing “big data”, whereby a smaller subset of a dataset is used to estimate the characteristics of its entire population. The main goal in sampling is often to achieve a significant gain in computational time. However, a major obstacle towards this goal is the assessment of the smallest sample size needed to ensure, with a high probability, a faithful representation of the entire dataset, especially when the data set includes a large number of diverse structures (e.g., clusters). To address this problem, we propose a method referred to as the Sparse Withdrawal of Inliers in a First Trial (SWIFT) that determines the smallest sample size of a subset of a dataset sampled in one grab, with the guarantee that the subset provides sufficient number of samples from each of the underlying structures necessary for the discovery and inference.
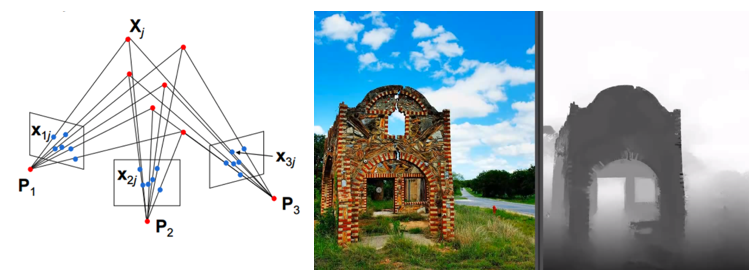
View Synthesis by 3D Image Reconstruction
One very challenging and critical process in 3D computer vision is estimating new view synthesis given multiple images of a 3D scene. In this process, the goal is to synthesize an image of the object/scene after a specified transformation of viewpoint. These new synthetic views can be used for applications in computer vision, graphics, and robotics. New view synthesis is an extremely challenging problem. An exact solution would require full 3D knowledge of all visible geometry in the unseen view, which is generally unavailable due to occlusions. Additionally, visible surfaces may have ambiguous geometry due to a lack of texture.
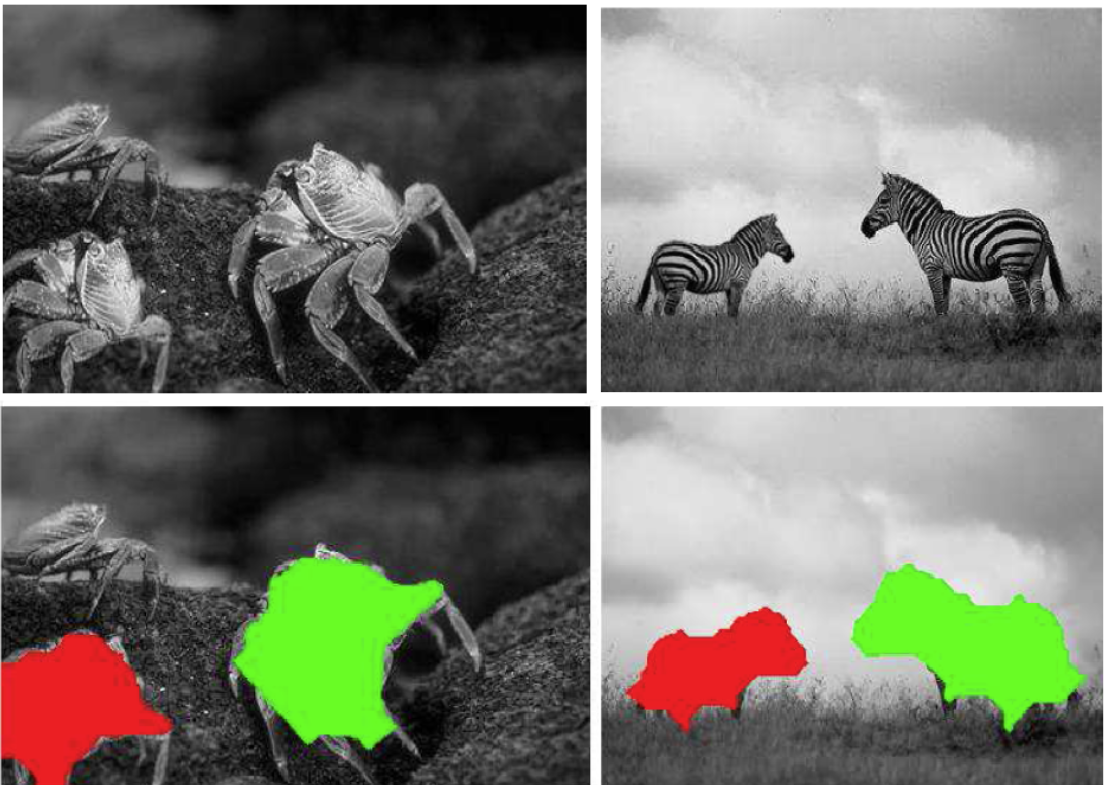

Copy-Move Image Forgery Detection
In this research, we have adopted keypoint-based features for copy-move image forgery detection; however, our emphasis is on accurate and robust localization of duplicated regions. In this context, we are interested in estimating the transformation (e.g., affine) between the copied and pasted regions more accurately as well as extracting these regions robustly by reducing the number of false positives and negatives. To address these issues, we propose using a more powerful set of keypoint-based features, called MIFT, which share the properties of SIFT features but also are invariant to mirror reflection transformations. Moreover, we propose refining the affine transformation using an iterative scheme which improves the estimation of the affine transformation parameters by incrementally finding additional keypoint matches.